Five Ws Single Sign On
Single-Sign-on (SSO) is a mechanism of authentication method that enables users to securely authenticate with multiple application or website by using just one set of credentials.
What
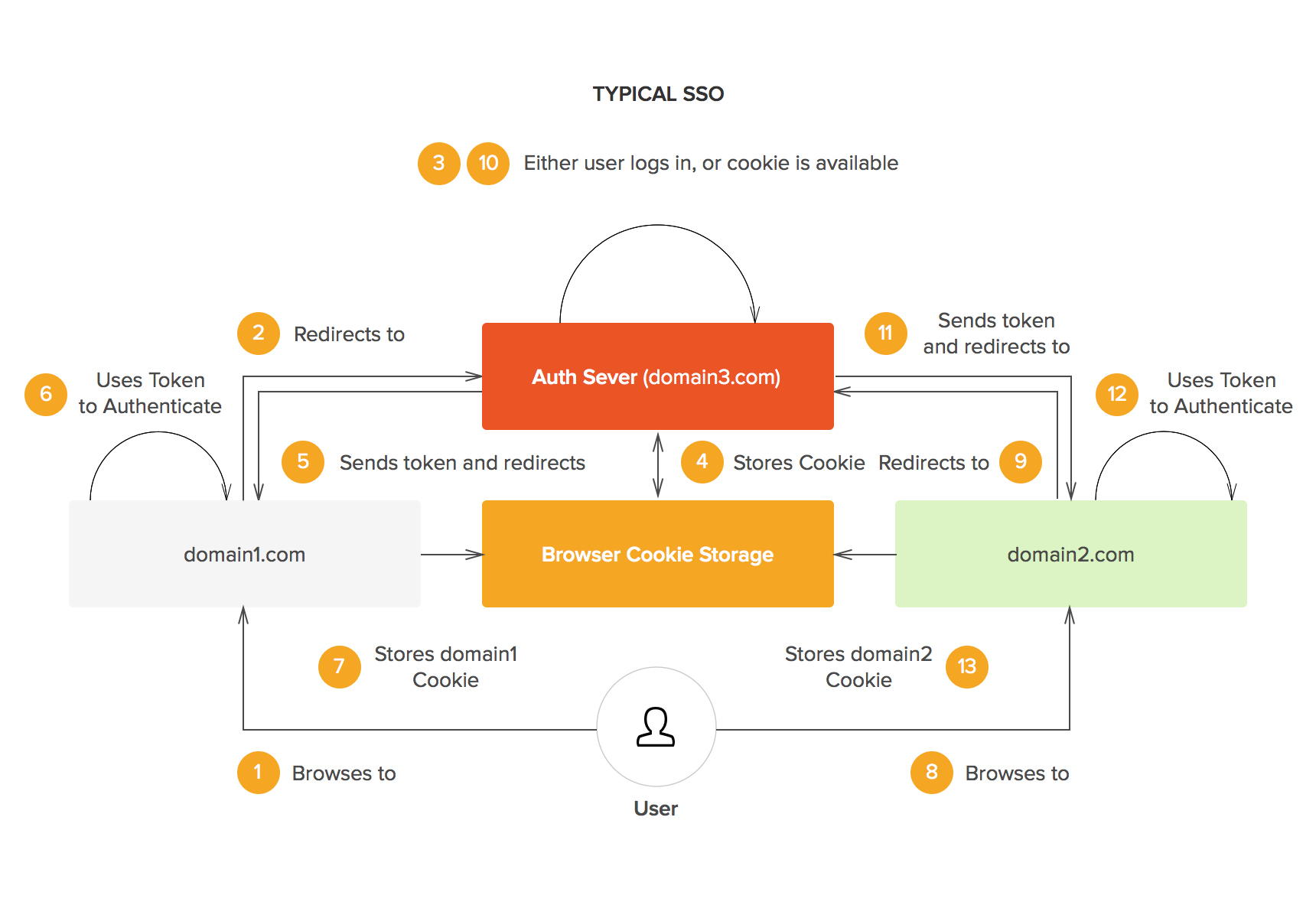
Simple Authentication Flow
Single-Sign-on (SSO) is a mechanism of authentication method that enables users to securely authenticate with multiple application or website by using just one set of credentials.
Authentication vs Authorization

| Authentication | Authorization | |
|---|---|---|
| What does it do? | Verifies credentials | Grants or denies permissions |
| How does it work? | Through passwords, biometrics, one-time pins, or apps | Through settings maintained by security teams |
| Is it visible to the user? | Yes | No |
| It is changeable by the user? | Partially | No |
| How does data move? | Through ID tokens | Through access token |
Terminology
Identity and Access Management
Is a solutions that are used to manage user identities and access to IT resources. The IAM category consists of number of subcategory, including IDP (Identity Provider), Identity as a Service, Priviledges Identity/Access Management (PIM/PAM), Multi-factor Authentication and many more.
Identity Provider
User identity information is stored and managed by a centralized system called IDP (Identity Provider). It’s authenticates the user and provides access to the service provider. The IDP can directly authenticate the user by validating a username and password or by validating an assertion about the user identity as presented by separated IDP. Also handling the management of user identities.
Service Provider
It’s an application or a provider who provide a services to end-user. SP rely on Identity Providers to assert the identity of user. Also maintain a local account for the user along with attributes are unique to their service.
Differents type of protocols
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) 2.0
Is an XML based (WSDL), open-standard data format for exchange authentication and authorization data between parties. This XML document is digitally signed by the Identity provider and shared with Service provider during the user authentication process.
OAuth 2.0
Is an authorization framework that enable application to obtain limited access to user accounts on an HTTP services. It’s allows third party application to authorize users by providing an access token. The application can only access limited user information which is permitted by the user themselves.
OpenID
Is an open standard and decentralized authentication protocol controlled by the OpenID Foundation.
OpenID Connect(OIDC)
Is an identity layer that operates on top OAuth 2.0 (it’s combines the feature of OpenID and OAuth). It provide basic profile information about the end-user by specifying RESTful API’s that use JSON as data format (Usually using JWT).
| Features | SAML | OAuth |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | authentication protocol | authorization protocol |
| Usage Scenario | will be used by those who are looking for federation and identity management. They will use the identity to log in the users to different app | will be used by those who are not looking to maintain identities but are rather trying to leverage the implementation of the secure protocol by applications such as Google, Microsoft, Paypal, which ensure that the identities are authentic. |
| Suitable Application | popular for browser-based applications. | suitable for both browser and mobile applications. |
| Commonly used by | widely used for enterprise applications. | widely used for customer applications and API access. |
| Data Format | uses XML to transfer messages between applications. | uses JSON to transfer messages between applications. |
Why
Challenges
- Extra-strong passwords must enforced, if an SSO account is hacked, others under the same authentication system can also be targeted. One way to reduce this risk is by implementing Multi Factor Authentication (MFA).
- When SSO is down, access to all connected sites is stopped, it must be realible and plans should be in place for dealing with issues.
- If a hacker breaches your identity provider user account, all your linked systems could be open to attack. This can be a classic single point of failure and should be headed off in the planning process. On the plus side, high-quality identity providers have top-notch security.
Advantage
- Simple, remembering one password instead of many make user’s lives easier. It’s also simplify the operations, just need manage credentials in one place, also reducing Help Desk Cost.
- Speed, no more input another credential for another app. Users can sign up quickly as they can login to another app, increasing user adoption & usability.
- Transparency, Users know what’s being shared from one app to another.
Who
It’s kinda clear for now, OpenID Connect is the choosen one. We need both authentication and authorization, the next concern is what we need fist, is IDP sufficient or IAM (the complete solutions).
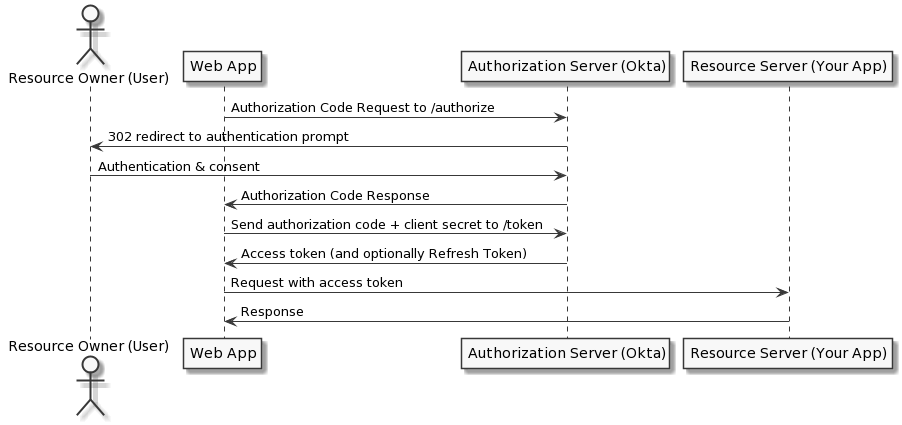
Authorization Code Flow
The option for OpenID Connect
| Features | WSO2 | Keycloak | Gluu | Hydra |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | IAM with decoupled feature | IAM | IAM | IAM with decoupled feature |
| Multi-factor auth | SMSOTP, FIDO, MEPin, complete list | Google Auth, FreeOTP, U2F | FIDO2, Google Auth, HW Dongle complete list | On Progress |
| User Management | web UI, API | web UI, API | web UI, API | web UI, API |
| Middleware | WSO2 Carbon | Wildfly, JBOSS | Jetty, Apache HTTPD | Standalone |
| Vendor | WSO2 | Redhat | Gluu Inc | Ory |
| Open source | Apache Licence Commercial | Apache Licence Commercial | Community Edition Pricing | Open source with support |
| Modularity | yes | no, all in one bundle | no, all in one bundle | yes |
| Languange | Java | Java | Java | Golang |
| Docker Support | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Development Support | difficult | difficult | difficult | easy |
Where
In Where the SSO can be used?
The answer is every apps can using the SSO, as long the app not maintaining user credentials (login / registration etc).
What if already bunch of apps already have their own user credentials?
The answer is on How
How
Integration / Migration plan (the options)
Auto register existing users
- Create callback to hit to API Auth Server (new API for auto register – Auth Server), this is will triggered after user successfully login in existing apps.
- Develop new auth base on Auth Flow
- Implementation / Go Live!
- What’s happened with existing user, but the users is not yet active (no login activity) within callback implementation?
Export / Import existing users
- Export existing user to xls (Bulk) and import to Auth Server
- Sent email for generating password (UI / Apps for generating new password)
- Develop new auth base on Auth Flow
- Implementation / Go Live!
Another Notes
- Option in app for using their identity system or SSO
- Option for choosing UI Login App (Auth Server) or their Own Login page
- Enforce password policy
- Development Portal Auth Server
Implementing Single Sign On is never easy, but the business need it